Information
Journal Policies
Using Avocado Leaves to Prevent Streptococcus Viridans' Inhibition in Growing Caries in Mouth
Prasko1,Irmanita Wiradona2,Suwarsono3
Copyright :© 2017 Authors. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Background: Bacteria play an essential role in the process of dental caries. Caries prevention efforts are made in many ways using an antiseptic or herbal mouthwash including avocado leaves that have the effect of antifungal, antimicrobial, analgesic, and anti-inflammatory.
The Objective: This study aims to determine the effectiveness of avocado leaf extract concentration of 60% and 80% for blocking the inhibition of the Streptococcus viridans, the bacteria that has a crucial factor in the formation of dental caries.
Method: The research was a quasi-experimental research using two samples in each treatment group. The sample consisted of 3 treatment groups of young avocado leaf extract concentration of 60%, 80%. Methods of data analysis used descriptive quantitative research.
Result: The results showed that the leaf extract of avocado with a concentration of 60% does not affect inhibiting the growth of bacteria Streptococcus viridans with an average of inhibition of 26.43mm. However, the avocado leaves extract with a concentration of 80% affect the growth of Streptococcus viridans bacteria with an average inhibition of 27.6 mm.
Conclusion: The conclusion of this study proves that avocado leaf extract has potent antibacterial activity against the growth of Streptococcus viridans.
Avocado Leaves, Streptococcus Viridans, Inhibition,Surgery
Organizing activities of oral health efforts can be reached in various ways including the traditional way which is well aligned with conventional medicine. Traditional medicine is material in the form of the plant, mineral materials, or mixtures of these substances that have historically been used for treatment, and can be applied by the norms of society (Permenkes RI, 2010).
Avocado is a fruit plant that belongs to the family Lauraceae that grow in the plains with the cold weather (Antia et al., 2005). Avocado plant parts that have many benefits is the leaves for the effect of antifungal, antimicrobial, analgesic, and anti-inflammatory. Some studies have shown that in vitro test avocado leaf extract containing flavonoids and alkaloids that can inhibit the spread of the virus of herpes simplex (Miranda et al., 1997). Hasbi (2012) on test sensitivity juice leaves of avocado (Persea Americana miller) on the growth of Pseudomonas sp shows giving juice of the leaves of avocado with a concentration of 100%, 80%, 60%, 40% and 20% can inhibit the growth of Pseudomonas. Based on this empirical evidence, this research expands the use of the avocado leaves to the inhibition of Streptococcus viridans which is a member of the healthy flora of the most common in the upper respiratory tract playing a vital role to maintain the normal state of the mucous membranes. But some Streptococcus viridans plays a significant factor in the formation of dental caries (Jawetz et al, 2005).
The purpose of this study is to determine the effectiveness of avocado leaf extract concentration of 60% and 80% to the inhibition of the growth of Streptococcus viridans.
2. Materials And Methods
The study was a laboratory experiment to study design study design post only control design.
The population is the result of pure cultures of bacteria Streptococcus viridans provided in the Local Government Health Laboratory Semarang. The sample used was a colony of Streptococcus viridans taken from pure cultures, which have been isolated and cultured with media in Microbiology Laboratory of the State University of Semarang.
The independent variables in this study were young avocado leaf extract Concentrations of 60% and 80%. The dependent variable is the bacterium Streptococcus viridans. The controlled variable is the culture medium of PCA, a 1 x 24-hour incubation and incubation temperature of 37 0C. The data is analyzed using quantitative descriptive analysis which describes the results of research in the form of numbers where the data obtained were processed and included in the table and then calculated the scores or the average value and tabulation.
3. Results And Discussions
There have been researching laboratories to test the inhibition of Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus viridans using extraction of avocado leaves. Inhibition test performed for each bacterium using Petri dishes with three steps are performed as follows:
1. 150 grams of dried avocado leaves were crushed.
2. 300 ml ethanol was extracted with soxhletation method Soxhletation was performed for approximately 3 hours
3. Results in evaporated solvent are extracted with rotary evaporator bath in temperature of 80°C
4. Viscous extract of avocado leaves is used to test the inhibition of bacteria.
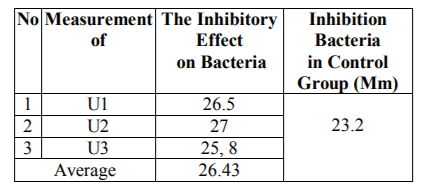
The table above shows that the bright zone after treatment with a concentration of 60% indicates an average value of 26.43 mm, where the smallest area of 25.8 mm, and the most extensive area of 27 mm. This condition, when compared to controls with an area of 23.2 mm relatively, showed less significant changes.
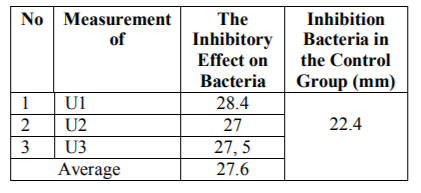
The table above shows that the transparent zone after treatment with concentration 80% showed an average value of 27.6 mm, where the smallest area of 27 mm, and the largest area of 28.4 mm. This condition, when compared to controls by 22.4 mm area relatively, showed less significant changes.
The results showed that the leaf extract avocado treatment with a dose of a mixture of 80% produced significant changes in the administration of avocado leaf extract against inhibition Streptococcus viridans obtained inhibition area average of 27.6. According to the classification power resistor, the bacterial inhibition zone was classified into three criteria: moderate (6-9 mm), active (10-14 mm) and very strong (15-18 mm) (Lade et al, 2006). This condition is because of the presence of several active ingredients of the leaves avocado such as flavonoids, saponins, alkaloid, and others. The presence of antibiotic substances in the avocado leaves as mentioned in theory explaining active elements contained in the leaves of avocado (Persea America miller) is a flavonoid, quercetin. Flavonoid in the human body functions as an antioxidant that is very good for preventing cancer. The benefits of flavonoids among others are to protect the cell structure, improve the effectiveness of vitamin C, anti-inflammatory, preventing bone loss, and as antibiotics. Flavonoids can act directly as an antibiotic to interfere with the function of microorganisms such as bacteria and viruses (Mursito, 2007). The results are also following previous studies which stated that avocado leaf contains several elements carried ( Maryati et al. 2007) in the study of the chemical constituents of avocado leaves showed that crude drugs avocado leaves contain flavonoids, saponins, and steroid or triterpenoid.
The active ingredient of avocado leaves will make the cell walls of bacteria damaged. One of the active substances that can harm the cell walls of bacteria is flavonoids and saponins. So with the damage to the bacterial cell wall, it will make the bacteria in the radius closest to the treatment (extracts from avocado) death.
The role of active substances such as flavonoids and saponins in avocado leaves is described in the theory that flavonoid was causing damage to the permeability of the bacterial cell wall, microsomes, and lysozyme as a result of the interaction of flavonoids with the DNA of bacteria. Saponin included in the group of antibacterial disrupt membrane permeability microbes results in damage to the cell membrane of the bacteria. The flavonoid compound serves as a bacteriostatic that damage the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane (Pelzar, 1996).
4. Conclusion
Based on the research that has been done in the laboratory of Semarang State University, the following results are obtained.
1. Extract of avocado leaves with a concentration of 60% does not affect blocking the growth of Streptococcus viridans bacteria with an average inhibition of 26.43 mm.
2. Extract of avocado leaves with a concentration of 80% affects the slowing growth of Streptococcus viridans bacteria with an average inhibition of 27.6 mm.
References
- Antia, BS. Je Okokon. Dan PA Okon. 2005. Hypoglycemic activity of aqueous leaf extract of Persea Americana Mill. Research Letter, Volume 37, Issue 5, Page 325-326. www.ijp-online.com
- Jawetz, E., Melnick, J.L., Adelberg, E.A., 2005, Mikrobiologi Kedokteran Edisi 20, Terjemahan oleh Nani Widarini, EGC, Jakarta.
- Maryati, S., Fidriany, I., & Ruslan, K. 2007. Penelitian Obat Bahan Alam Sekolah Farmasi ITB. Telaah kandungan kimia dau alpukat (persea americana mill). Fakultas Farmasi, Bandung. Institut Teknologi Bandung. (Skripsi).
- Miranda, M.M.F.S. S.S. Costa., M.G.M. Santos., M.H.C. Lagrota., A.P. Almeida., dan M.D. Wigg. 1997. In Vitro Activity Of Extracts Of Persea Americana Leaves On Acyclovir-Resistant And Phosphonoacetic Resistant Herpes Simplex Virus. Journal Phytomedicine, Vol. 4,pp. 347–352.)
- Hasbi, S. 2012. Uji Sensitivitas Perasan Daun Alpokat (Persea americana miller) terhadap Pseudomonas sp Metode Invitro. Karya Tulis Ilmiah. Akademi Analis Kesehatan. Banda Aceh.
- Lade, H.S., Chitanand, M.P., Gyananath, G., Kadam, T.A., (2006), Studies on Some Properties of Bacteriocins Produced by Lactobacillus Species Isolated from Agro-Based Waste, The Internet Journal of Microbiology, www.bioline.org
- Mursito, Bambang. 2007. Ramuan Tradisional Untuk Pengobatan Jantung. Jakarta : Penebar Swadaya
- Pelzar dan Chan, 1996. Dasar-dasar Mikrobiologi. Jakarta: UI Press.
- PERMENKES RI (2010). Saintifikasi Jamu Dalam Penelitian Berbasis Pelayanan Kesehatan.