Information
Journal Policies
Case Report: Role of 3D HD Live in Diagnosis of Iniencephaly
Mahmoud Alalfy1,*, Alaa Hamed2, Mohamed Elhodeby3, Adel Hosny4, Ihab Younes5, Mohamed Ezz Eldin6
2.Lecturer of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Alazhar University, Egypt.
3.Lecturer of obstetrics and Gynecology, Misr University, Fellow at caifm, Egypt.
4.Consultant of obstetrics and Gynecology, Fellow at caifm, Egypt.
5.Assistant lecturer of obstetrics and Gynecology, Misr University, Egypt.
6.Specialist of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Aljazeerah Hospital, Egypt.
Copyright : © 2018 . This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Iniencephaly is characterized by severe retro flexion of the head with the absence of neck due to spinal vertebrae deformities.
Associated Anomalies: Anencephaly, encephalocele, cyclopedia, lack of lower jaw bone, cleft palate, arthrogryposis, clubfeet, holoprosencephaly, spina bifida, lung hypoplasia, omphalocele, gastroschisis, cardiovascular disorders, Congenital diaphragmatic hernias, gastrointestinal atresia, single umbilical artery and renal abnormalities.
Conclusion: Iniencephaly is a lethal congenital neural tube malformation. It is characterized by occipital bone defect, fixed retroflexion of the fetal head and severe lordosis of the cervicothoracic spine.
Differential Diagnosis: Include anencephaly with cervical spinal retro flexion and Klippel-Fiel syndrome.
neural tube defect, iniencephaly, spina pifida, anencephaly.
1. Definition
Iniencephaly is characterized by severe retro flexion of the head with the absence of neck due to spinal vertebrae deformities, it is considered as uncommon anomaly.
Prevalence: 0.1-10:10,000, M: F.
Etiology: Unknown, but genetic, environmental factors are implicated.
Pathogenesis: Unknown. Recurrence risk: 1-4%.
2. Introduction
Iniencephaly is a rare and lethal congenital malformation of the neural tube characterized by occipital bone defect, cervical dysraphism, fixed retroflexion of the fetal head and severe lordosis of the cervicothoracic spine [2].
There are two types of iniencephaly [3]. Iniencephaly apertus, shows encephalocele and is considered the most severe type. The other group is not associated with the encephalocele (iniencephaly clauses). Iniencephaly may be accompanied with anencephaly, encephalocele (cranial brain tissue extrudes from the skull), cyclopedia (fusion of the two eye cavities into one), lack of lower jaw bone, cleft palate, arthrogryposis, clubfeet, holoprosencephaly, spina bifida, low set ears, pulmonary hypoplasia, omphalocele, gastroschisis, cardiovascular disorders, diaphragmatic hernias, gastrointestinal atresia, single umbilical artery and renal abnormalities [1].
3. Case Report
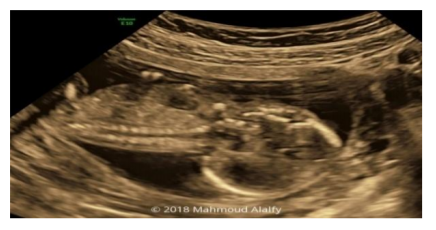
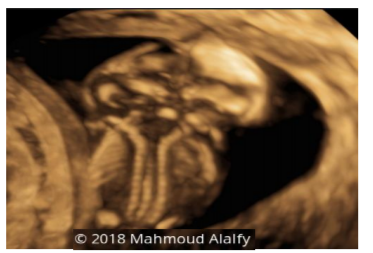
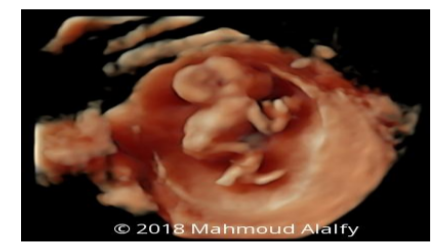
26 years old female pregnant 14 weeks came to National Research Centre fetal medicine unit for routine anomaly scan, the ultrasound finding revealed a single living fetus 14 weeks by CRL and shows absent fetal neck with severe retroflexion of the head.
Also US examination revealed restricted upper and lower limbs movements.
The parents were counseled about the poor prognosis and they decided to terminate pregnancy, Induction of abortion was made after approval of religious committee, and baby was delivered by vaginal delivery at Algazeerah hospital.
4. Discussion
The term of Iniencephaly is taken from the Greek word inion which means back of the neck and encephalos refer to brain. The fusion of the posterior most part of occipital bone with the back leading to the absence of the neck and retroflexion of head [4].
The diagnosis of iniencephaly antenatally by ultrasonography/Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) or Computed Tomography (CT). The fetus will show typical star gazing appearance on USG and detailed CNS and spine abnormalities may be known by Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) or Computed Tomography (CT) [5].
The keys for diagnosis a case of iniencephaly by ultrasound includes:
1. Irregular fusion of malformed vertebrae.
2. Incomplete closure of vertebral arches and bodies.
3. Retroflexion of the cervical spine.
Upward turned face with chin continuous with chest because of the absence of neck [6]. Our case had all these features and hence was diagnosed as iniencephaly.
Iniencephaly apertus should be differentiated from anencephaly with retroflexion of spine. Also, iniencephaly clausus should be differentiated from Klippel-Fiel syndrome (KFS) and cervical meningomyelocele. Anencephaly shows a total or partial absence of neurocranium and retroflexed head is not covered with skin. However, in iniencephaly the retroflexed head is completely covered with skin. Cervical vertebrae are abnormal in iniencephaly and they are almost normal in anencephaly. In the present case the retroflexed head was completely covered with skin and there was encephalocele. Klippel-Fiel syndrome is characterized by the congenital fusion of any 2 of the 7 cervical vertebrae.
Iniencephaly apertus is always fatal in the neonatal period [7] and our case was diagnosed as iniencephaly apertus and the termination of pregnancy was suggested and the procedure was explained to her. Four cases with a mild iniencephalus clausus have been reported with long-term survival, although in these cases, the deformity was minimal and they should probably have been classified as Klippel-Feil syndrome [8].
References
- Baker PN. Prenatal diagnosis. In: Obstetrics by 10 teachers. Book. Power. Publishers. Hodder Arnold. London. 18, 107-108 (2006).
- Balci S, Aypar E, Altinok G et al. Prenatal diagnosis in three cases of iniencephaly with unusual postmortem findings. Prenat. Diagn. 21, 558-562 (2001).
- Moore CA. Neural tube defects from origin to treatment. Cerebrospinal. Fluid. Res. 3, 6 (2006).
- Pungavkar SA, Sainani NI, Karnik AS et al. Antenatal diagnosis of iniencephaly: Sonographic and MR correlation: A case report. Korean. J. Radiol. 8, 351-355 (2004).
- Gadodia A, Gupta P, Sharma R et al. Antenatal sonography and MRI of iniencephaly apertus and clausus. Fetal. Diagn. Ther. 27, 178-180 (2010).
- Chen CP. Prenatal diagnosis of iniencephaly. Taiwan. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 46, 199-207 (2007).
- Nishimura H, Okamoto N. Iniencephaly - Handbook of Clinical Neurology. New. York. North Holland. Biochemical. Press. 30, 257- 268 (1977).
- Katz VL, Aylsworth AS, Albright SG: Iniencephaly is not uniformly fatal. Prenat. Diagn. 9, 595-599 (1989).